Huntington's Disease Dna Sequence
Huntington's disease dna sequence. Affordable Sample To Result In a Day From Applied Biosystems. The influence of HTT interrupting sequence variants on age of onset in Huntingtons disease. Anúncio Genetic Disease Research Can Be Complex Your Sequencing Approach Need Not Be.
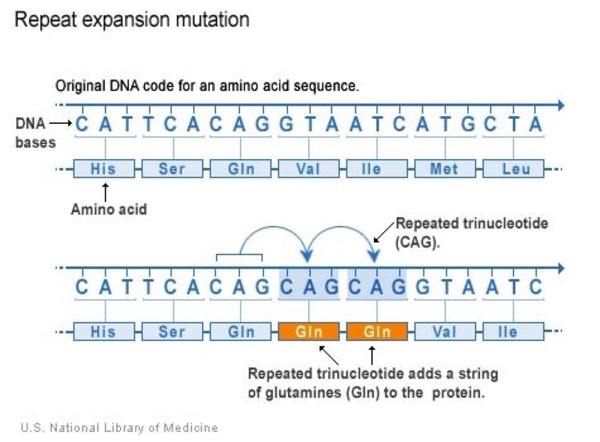
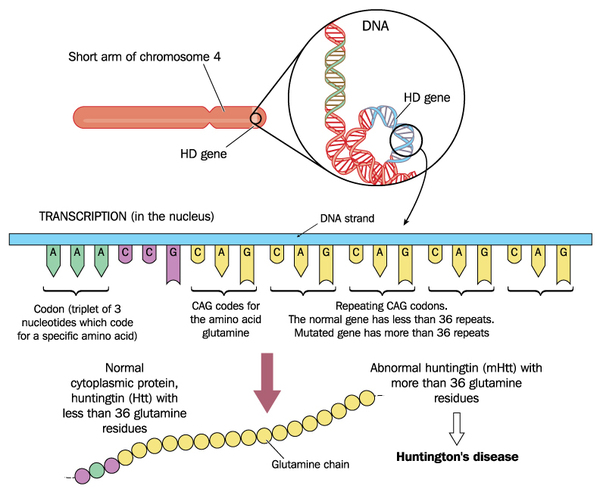
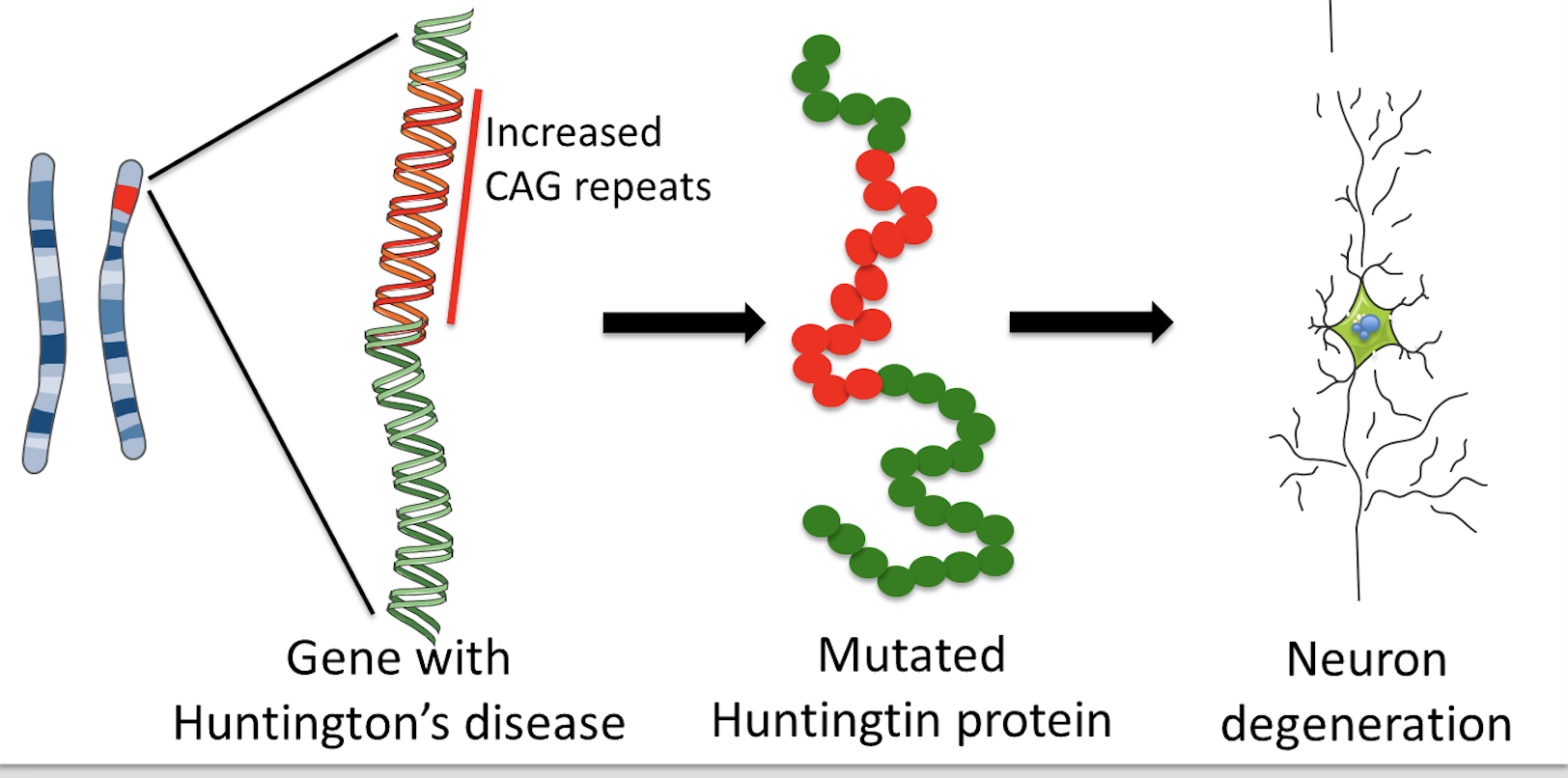
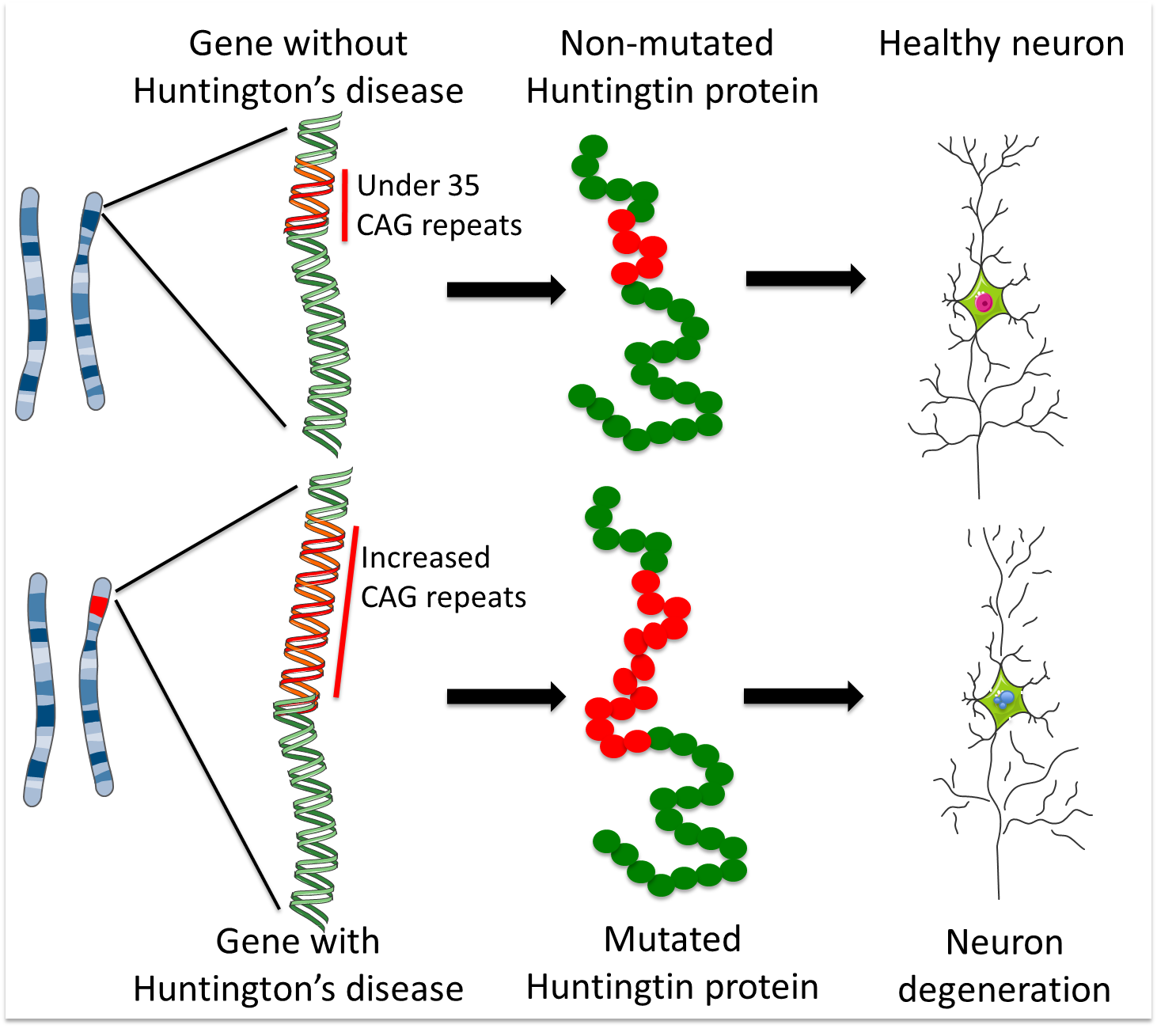
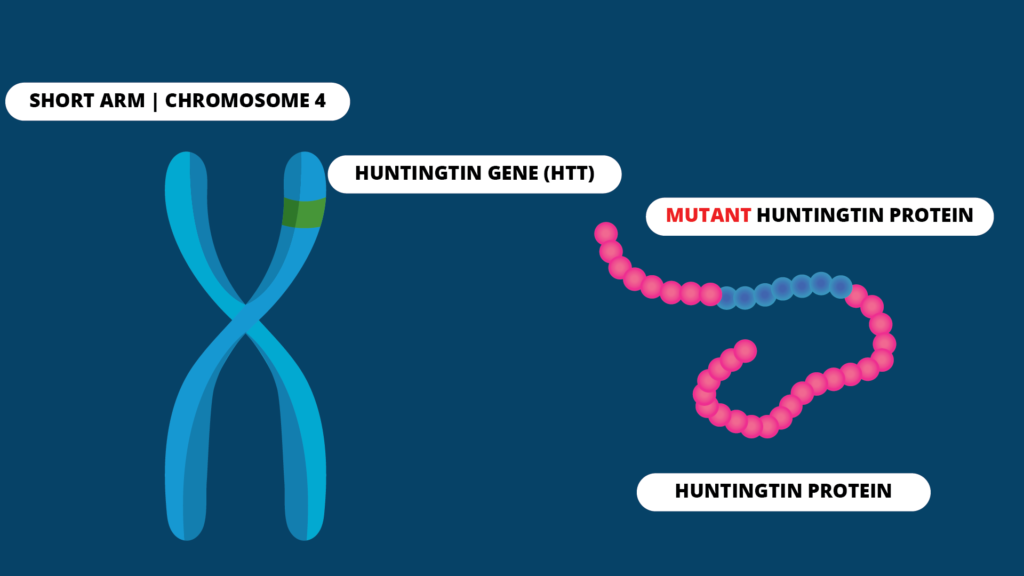
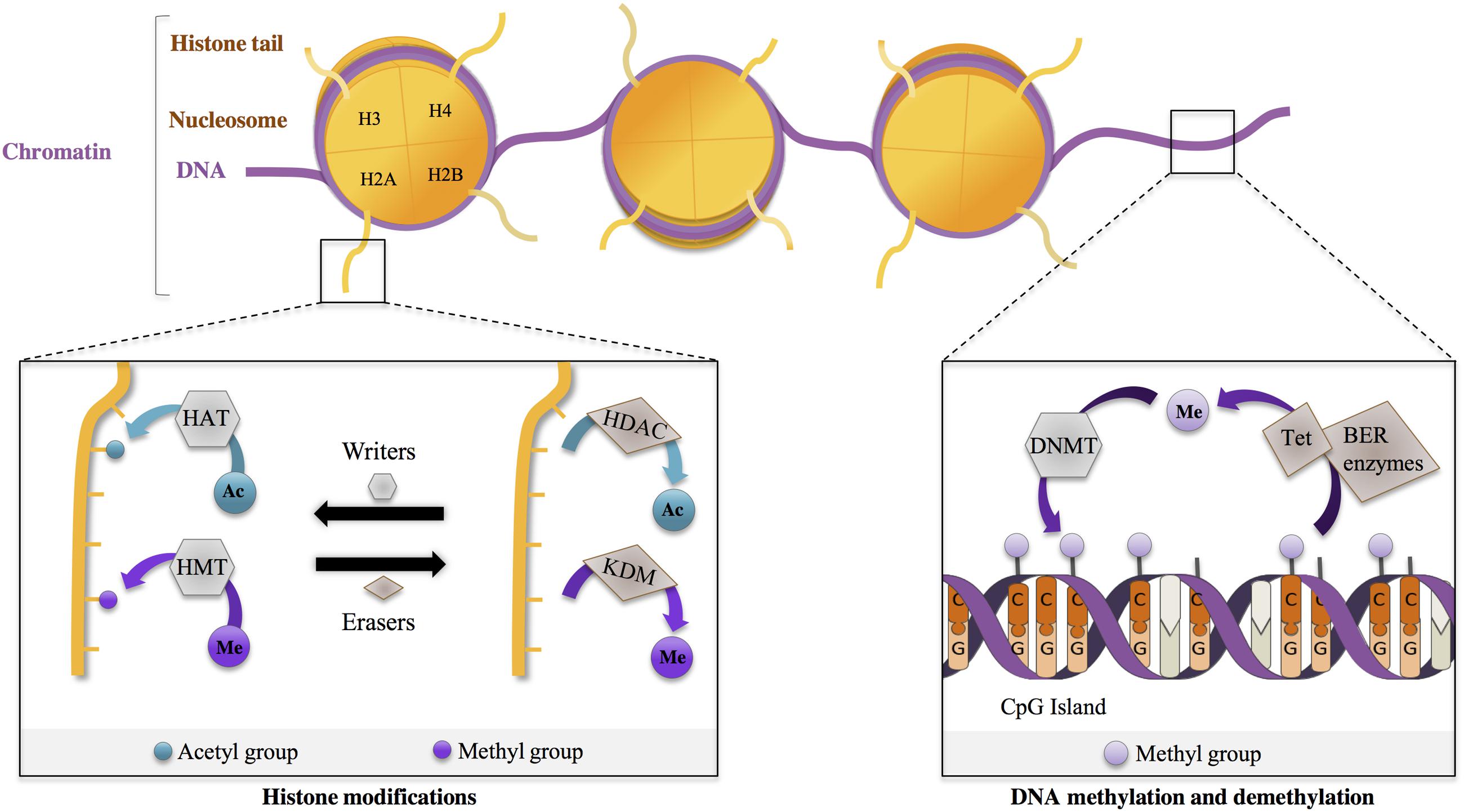
The discovery of the HD gene led to a genetic test to make or confirm the diagnosis of Huntingtons disease. The gene responsible for HD contains a sequence with several CAG repeats Cytosine Adenine Guanine. However 36 or more residues produce an erroneous mutant form of Htt mHtt.
Huntingtons disease is linked to a mutation in the HTT gene that codes for the huntingtin protein. Everyone has this sequence but the number of times it is repeated varies. It is a rare disease with only 1 in 10000 people affected and is caused by an increase in the.
Affordable Sample To Result In a Day From Applied Biosystems. Mutations in the HTT gene are responsible for Huntingtons Disease. Results from three independent genetic studies of Huntingtons disease have shown that glutamine-encoding CAA variants that interrupt DNA CAG repeat tracts but do not alter polyglutamine length or polyglutamine homogeneity are associated with substantial differences in age of onset of Huntingtons.
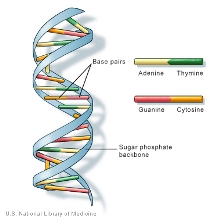
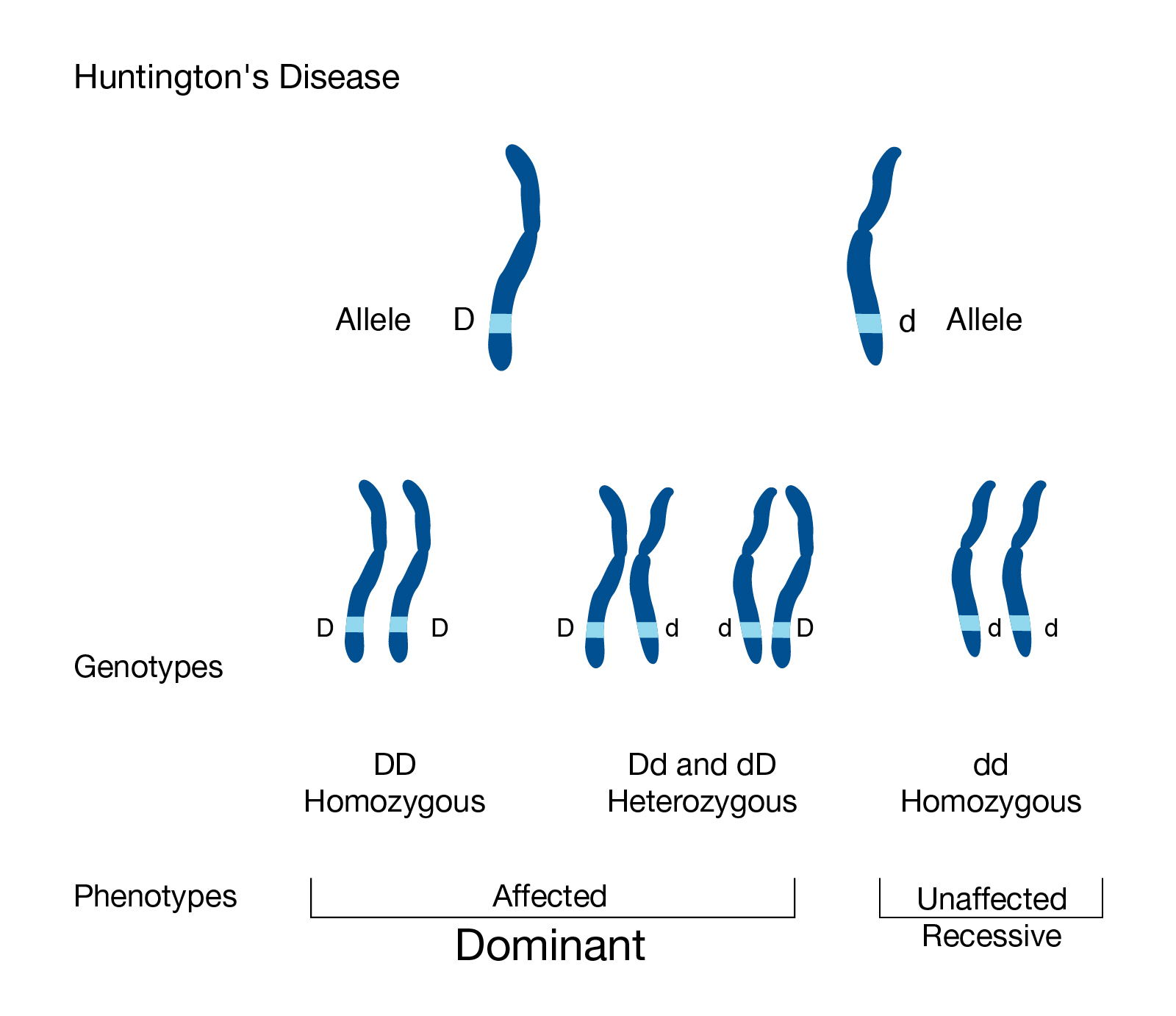
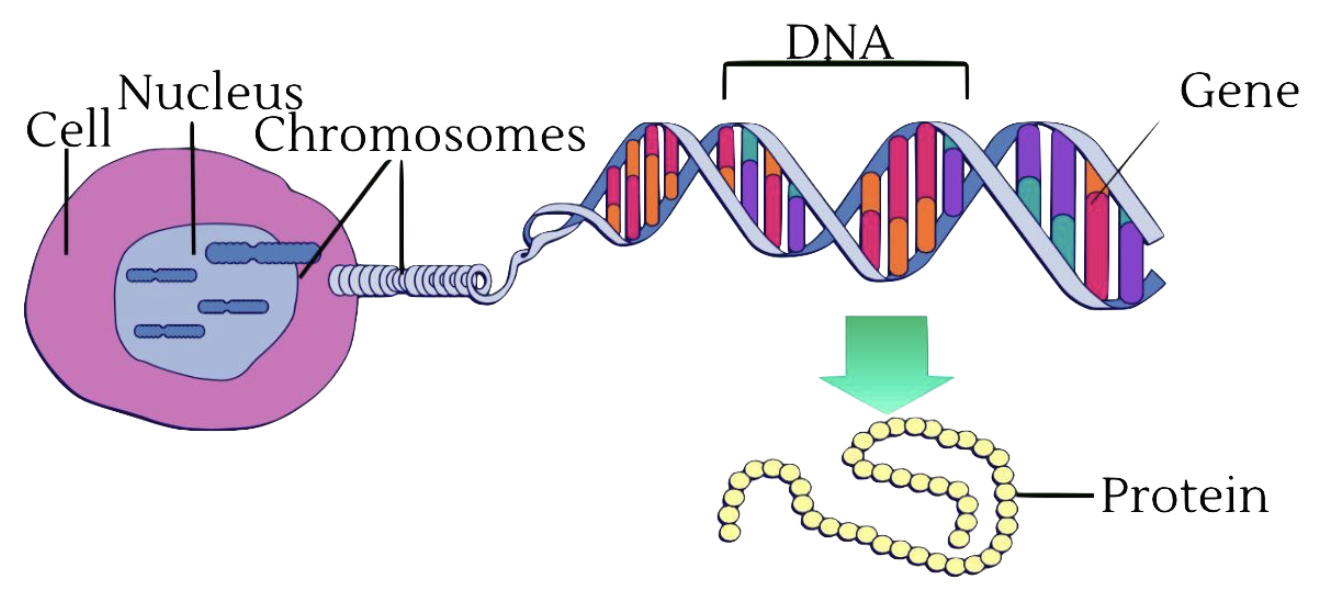
In unaffected individuals this contains between 9 and 35 glutamine residues with no adverse effects. DNA is made from a sugar phosphate backbone the sides of the ladder combined with pairs of nitrogen bases that hold the two sides together the rungs of the ladder. Huntingtons disease has autosomal dominant inheritance meaning that an affected individual typically inherits one copy of the gene with an expanded trinucleotide repeat the mutant allele from an affected parent.
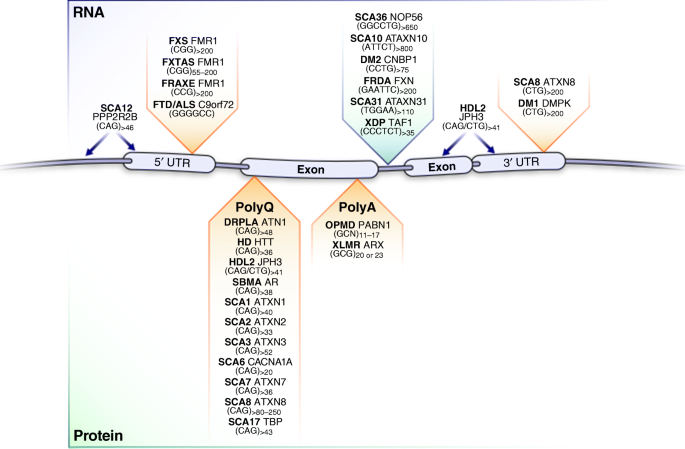
These repeat expansion disorders can have repeat units of different size and sequence that can be located in any part of the gene and while the pathological consequences of the expansion can differ widely there is evidence to suggest that the underlying mutational mechanism. The Huntingtons gene - the gene that determines whether you will develop Huntingtons disease - is attached to chromosome pair number 4. The genetic code or DNA sequence provides instructions for a series of amino acids the building blocks of proteins.
Since the penetrance of the mutation is very high those who have a mutated copy of the gene will have the disease. This is thought to be caused by an expanded unstable trinucleotide repeat in the huntingtin gene which translates as a polyglutamine repeat in the protein product.
Adenine Thymine Guanine and Cytosine.
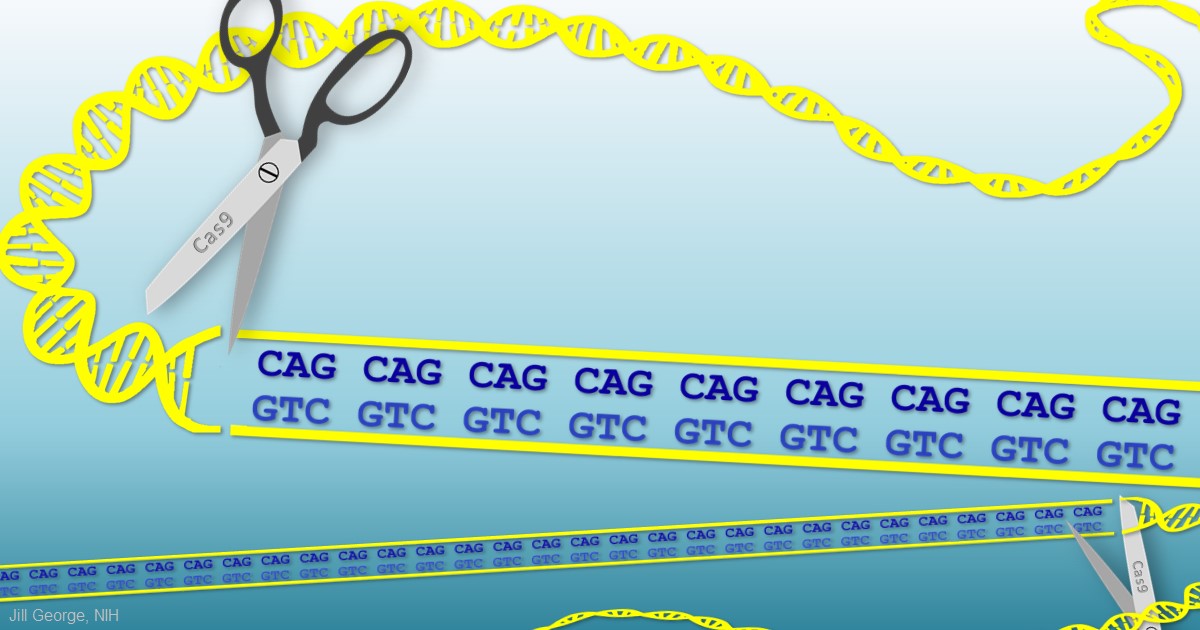
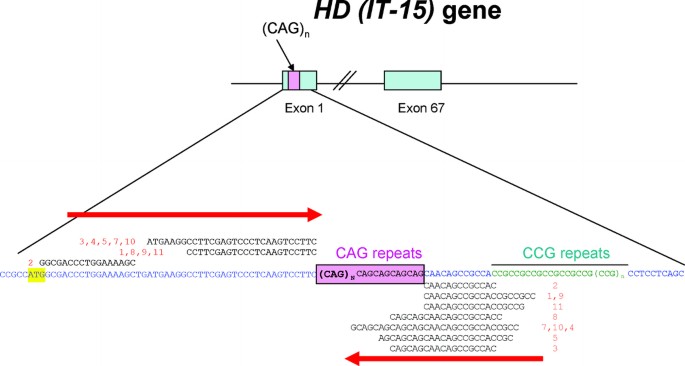
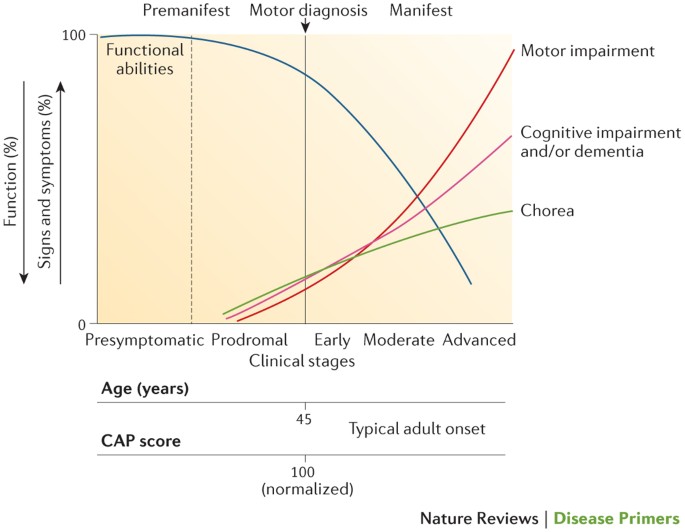
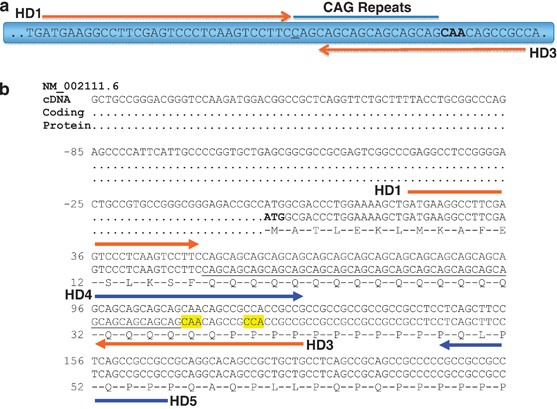
This segment is made up of a series of three DNA building blocks cytosine adenine and guanine that appear multiple times in a row. However 36 or more residues produce an erroneous mutant form of Htt mHtt. Genes are usually attached to a chromosome a strand of DNA containing many different genes. Everyone has this sequence but the number of times it is repeated varies. Anúncio Genetic Disease Research Can Be Complex Your Sequencing Approach Need Not Be. The key sequence which is found in Huntingtons disease is a trinucleotide repeat expansion of glutamine residues beginning at the 18th amino acid. Huntingtin is a disease gene linked to Huntingtons disease a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by loss of striatal neurons. The HTT mutation that causes Huntington disease involves a DNA segment known as a CAG trinucleotide repeat. Clinically HD is defined by characteristic motor disturbances most notably chorea which typically begins to present when the individual is of 30 to early 40 years of age 2.
The HTT mutation that causes Huntington disease involves a DNA segment known as a CAG trinucleotide repeat. Longer sequences are rare and cause disease in younger individuals. Representation of the effect of the three interrupting sequence variantsie loss of interruption uninterrupted canonical CAA-CAG1 and duplication of interruption CAA-CAG2on age of onset in individuals with Huntingtons disease. Individuals who do not have HD usually have 28 or fewer repeats. Huntingtons disease is linked to a mutation in the HTT gene that codes for the huntingtin protein. This gene codes for the huntingtin protein and within the HTT gene is a DNA sequence known as the CAG trinucleotide repeat. The key sequence which is found in Huntingtons disease is a trinucleotide repeat expansion of glutamine residues beginning at the 18th amino acid.


























Post a Comment for "Huntington's Disease Dna Sequence"